GLAUCOMA
Bringing Your Vision to Life, One Service at a Time


Diagnostics
Advanced glaucoma diagnostics integrate several cutting-edge techniques to deliver a comprehensive assessment of a patient's ocular health, facilitating precise evaluation and effective management. Here is an in-depth look at each of the components involved.
Together, these diagnostic tools provide a detailed and multifaceted view of the patient's eye health. Understanding individual IOP levels, optic nerve structure, visual field integrity, and corneal attributes allows clinicians to tailor glaucoma management plans. This approach improves early detection, enables proactive intervention, and helps in the continuous monitoring of glaucoma to prevent vision loss.

Non-Contact Tonometry (NCT):
This method uses a puff of air to flatten the cornea and measure the resistance. It's non-invasive and convenient, providing a quick initial screening for higher IOP, which is a significant risk factor for glaucoma.

iCare Handheld Tonometers:
These tonometers are portable and use a small, disposable probe to gently touch the cornea, offering accurate pressure readings without the need for anesthetic drops. They are particularly useful in clinical settings for rapid assessments and follow-ups.

Goldmann Applanation Tonometry (GAT):
Considered the gold standard, GAT involves using a slit lamp-mounted device that directly measures the force needed to flatten a small area of the cornea. It provides highly accurate readings and is critical in diagnosing and monitoring glaucoma.
Intraocular Pressure (IOP) Measurements:
Accurate measurement of intraocular pressure (IOP) is crucial in diagnosing and managing glaucoma and other ocular conditions. Elevated IOP is a significant risk factor for optic nerve damage, making regular assessments an essential part of comprehensive eye care. Various tonometry methods are available, each offering unique advantages in clinical settings. Below are the primary techniques used to measure IOP, ranging from non-contact approaches to the gold standard in eye diagnostics.
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) by Nidek:
Optic Nerve Assessment: OCT provides high-resolution, cross-sectional images of the optic nerve head, retinal nerve fiber layer, and ganglion cell complex. These images allow for the detection of structural changes associated with glaucoma progression, often before functional impairments become apparent.

Visual Field Testing with Zeiss HFA 840:
Detecting Peripheral Vision Loss: This automated perimetry machine maps the visual field to identify any areas of vision loss, particularly in the peripheral field—a common early sign of glaucoma. Consistent monitoring of the visual field helps track disease progression and guide treatment adjustments.

Glaucoma Management
Effective glaucoma management involves a multifaceted approach that not only focuses on controlling intraocular pressure (IOP) but also emphasizes patient education and supportive care. Our dedicated team is committed to providing personalized treatment plans, continuous monitoring, and resources to help patients maintain optimal eye health. Below are the key components of our glaucoma management strategy, designed to ensure comprehensive care and improved quality of life for our patients

Laser Peripheral Iridotomy (LPI):
This procedure is often used for narrow or closed-angle glaucoma. A laser creates a small hole in the peripheral iris, allowing fluid to flow more freely through the eye's drainage angle, reducing IOP and preventing an acute angle-closure attack.

Trabeculectomy:
In this surgical procedure, a small flap in the sclera (white of the eye) is created, along with a drainage reservoir (bleb) in the conjunctiva (the outer lining of the eye), which allows fluid to drain and be absorbed into surrounding tissues, reducing IOP.

Glaucoma Drainage Devices (or Shunts):
These devices, like the Ahmed or Baerveldt implants, are placed inside the eye to provide a new drainage pathway. They consist of a small tube that drains fluid away from the front of the eye into a reservoir or plate underneath the conjunctival tissue, where it is absorbed into the bloodstream.
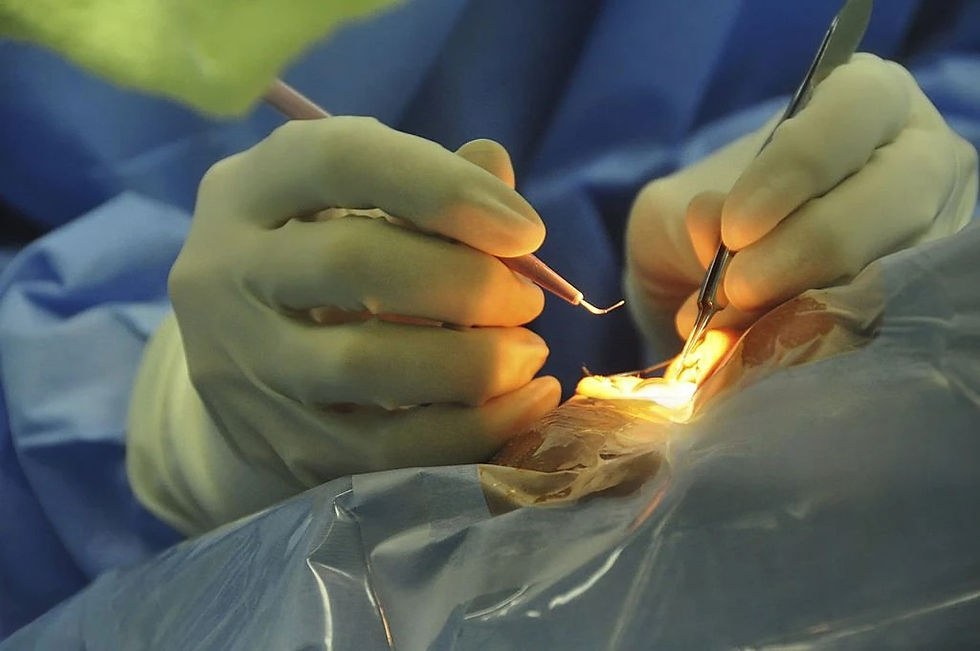
. Minimally Invasive Glaucoma Surgery (MIGS):
A newer category that includes procedures like the iStent or XEN Gel Stent, aimed at reducing IOP with less tissue manipulation compared to traditional surgeries. They offer quicker recovery times and fewer complications.
Corneal Thickness Measurement with Nidek Pachymetry:
Understanding Individual Risk Factors: Pachymetry measures the central corneal thickness, which is an important factor in interpreting IOP readings. Thinner corneas can lead to underestimations, while thicker corneas might indicate overestimations of IOP, affecting risk assessment and management strategies.


Treatment options for Glaucoma
These treatment options are selected based on the type and severity of glaucoma, the patient's overall health, and their response to initial therapies. The goal is always to tailor the approach to ensure effective management of IOP to preserve vision and quality of life for each patient. Regular follow-ups are essential to monitor disease progression and adjust treatments as needed. Treatment options for glaucoma are designed to lower intraocular pressure (IOP) and prevent optic nerve damage. Here’s more about the various approaches:
Regular Monitoring:
Ongoing monitoring of IOP, optic nerve health, and visual fields is crucial for managing glaucoma effectively. Our team conducts regular follow-up appointments to track any changes in your condition.
Patient Education:
We prioritize educating patients about glaucoma, its effects, and the importance of adhering to treatment regimens. Understanding the condition empowers patients to take an active role in their eye health.
Lifestyle Modifications:
Our specialists provide guidance on lifestyle changes that can support eye health.
Support Services:
We offer resources and support services for those living with glaucoma, ensuring that patients and their families have access to helpful information and community support.
